Arithmetic logic unit
Arithmetic logic unit refers to carry ripple adder designed earlier 1.
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity alu is
generic (
WIDTH: integer := 8
);
port (
a : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
b : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
cin : in std_logic;
ctrl : in std_logic_vector ( 1 downto 0);
cout : out std_logic;
q : out std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0)
);
end alu;
architecture behavioral of alu is
component carry_ripple_adder
generic (
WIDTH : integer
);
port (
a : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
b : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
ci : in std_logic;
s : out std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
co : out std_logic
);
end component;
signal operand1 : std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal operand2 : std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal operand2_complement : std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal sum : std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal sum_carry : std_logic;
signal difference : std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal difference_carry : std_logic;
begin
-- Connect inputs
operand1 <= a;
operand2 <= b;
-- Addition
adder1: carry_ripple_adder
generic map(
WIDTH
)
port map(
a => operand1,
b => operand2,
ci => '0',
s => sum,
co => sum_carry
);
-- Subtraction
operand2_complement <= not operand2;
adder2: carry_ripple_adder
generic map(
WIDTH
)
port map(
a => operand1,
b => operand2_complement,
ci => '1',
s => difference,
co => difference_carry
);
-- Control logic and inlined NOR and NAND operations
q <= sum when ctrl ="00" else
difference when ctrl ="01" else
operand1 nor operand2 when ctrl ="10" else
operand1 nand operand2 when ctrl ="11" else
(others => '0');
-- Carry bit
cout <= sum_carry when ctrl = "00" else
difference_carry when ctrl = "01" else
'0';
end;A simple testbench:
use work.all;
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all;
entity alu_testbench is
end;
architecture behavioral of alu_testbench is
constant TB_WIDTH : integer := 8;
signal a, b, q : std_logic_vector(TB_WIDTH-1 downto 0);
signal ctrl : std_logic_vector (1 DOWNTO 0);
signal cout, cin : std_logic := '0';
component alu
generic (
WIDTH: INTEGER:= TB_WIDTH);
port (
a : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
b : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
cin : in std_logic;
ctrl : in std_logic_vector ( 1 downto 0);
cout : out std_logic;
q : out std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0));
end component;
function to_std_logicvector(a: integer; length: natural) return std_logic_vector IS
begin
return std_logic_vector(to_signed(a,length));
end;
procedure behave_alu(a: integer; b: integer; ctrl: integer; q: out std_logic_vector(TB_WIDTH-1 downto 0); cout: out std_logic) is
variable ret: std_logic_vector(TB_WIDTH downto 0);
begin
case ctrl is
when 0 => ret := to_std_logicvector(a+b, TB_WIDTH+1);
when 1 => ret := to_std_logicvector(a-b,TB_WIDTH+1);
ret(TB_WIDTH):= not ret(TB_WIDTH);
when 2 => ret := '0' & (to_std_logicvector(a,TB_WIDTH) nand to_std_logicvector(b,TB_WIDTH));
when 3 => ret := '0' & (to_std_logicvector(a,TB_WIDTH) nor to_std_logicvector(b,TB_WIDTH));
when OTHERS =>
assert false
report "ctrl out of range, testbench error"
severity error;
end case;
q := ret(TB_WIDTH-1 downto 0);
cout := ret(TB_WIDTH);
end;
begin process
variable res: std_logic_vector ( TB_WIDTH-1 downto 0);
variable c: std_logic;
begin
for i in 0 to TB_WIDTH-1 loop
a <= to_std_logicvector(i,TB_WIDTH);
for j in 0 to TB_WIDTH loop
b <= to_std_logicvector(j,TB_WIDTH);
for k in 0 to 1 loop
ctrl<= to_std_logicvector(k,3)(1 downto 0);
wait for 10 ns;
behave_alu(i,j,k,res,c);
assert q = res
report "wrong result from ALU:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(res))) & " a:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(a))) & " b:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(b))) & " ctrl:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(ctrl)))
severity warning;
assert cout = c
report "wrong carry from ALU:" & std_logic'image(cout) & " expected:" & std_logic'image(c) & " a:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(a))) & " b:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(b))) & " ctrl:" & integer'image(to_integer(unsigned(ctrl)))
severity warning;
end loop;
end loop;
end loop;
report "ALU testbench finished";
wait;
end process;
uut: alu port map (a, b, cin, ctrl, cout, q);
end behavioral;Loading to ZYBO
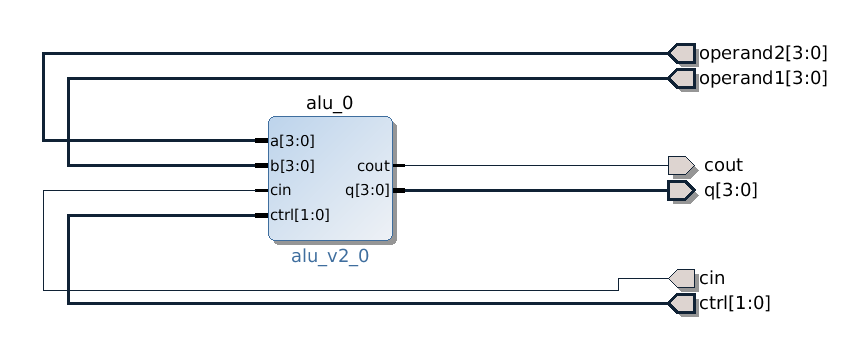
High level block design in Vivado
BTN4 and BTN5 seem to be unusable from FPGA portion since they're part of multiplexed I/O, so I had to resort to pins at Pmod connector JE.
Pin mapping at Constraints → constrs_1 → base.xdc:
# Operand1 at switch block
set_property PACKAGE_PIN R18 [get_ports {operand1[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN P16 [get_ports {operand1[1]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN V16 [get_ports {operand1[2]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN Y16 [get_ports {operand1[3]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {operand1[*]}]
# Operand2 at button block
set_property PACKAGE_PIN G15 [get_ports {operand2[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN P15 [get_ports {operand2[1]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN W13 [get_ports {operand2[2]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN T16 [get_ports {operand2[3]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {operand2[*]}]
# Output at LED block
set_property PACKAGE_PIN M14 [get_ports {q[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN M15 [get_ports {q[1]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN G14 [get_ports {q[2]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN D18 [get_ports {q[3]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {q[*]}]
# Instruction at JE1 and JE2
set_property PACKAGE_PIN V12 [get_ports {ctrl[0]}]
set_property PACKAGE_PIN W16 [get_ports {ctrl[1]}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {ctrl[*]}]
# Carry out at JE3
set_property PACKAGE_PIN J15 [get_ports {cout}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {cout}]
# Carry in at JB
set_property PACKAGE_PIN U20 [get_ports {cin}]
set_property IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 [get_ports {cin}]Numeric package
There actually is a IEEE package which already includes computer arithmetic. Here is example of same ALU sans carry logic.
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.numeric_std.all; -- Introduces data types signed and unsigned
entity alu is
generic (
WIDTH: integer := 8
);
port (
a : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
b : in std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0);
ctrl : in std_logic_vector ( 1 downto 0);
q : out std_logic_vector (WIDTH-1 downto 0)
);
end alu;
architecture behavioral of alu is
begin
q <= std_logic_vector(signed(a) + signed(b)) when ctrl ="00" else
std_logic_vector(signed(a) - signed(b)) when ctrl ="01" else
a nor b when ctrl ="10" else
a nand b when ctrl ="11" else
(others => '0');
end;